Trie树
据不完全统计,世界上现存英语单词的数量为17万到100万不等。假设现在要你写一个词典APP,要求能够快速检索、删除、添加单词,。显然你很容易想到两种方案:
- 将所有单词按字典序排列,在按二分搜索来查询。
- 奖励首字母索引表,在各索引项表内按字典序排序单词,再在当中按二分搜索查询。
但无疑上述方案的要求略高,需要大量的连续空间来存储数据,而且不方便添加删除操作。
这时Trie树便发挥作用了,我们可以用Trie树来存储单词数据,树结构不需要大量连续的存储空间而且查询、添加结点、删除结点的操作的时间复杂度很小为$O(\log_{2}{N})$。
举个例子:
假设存储
这几个单词。其逻辑结构为:
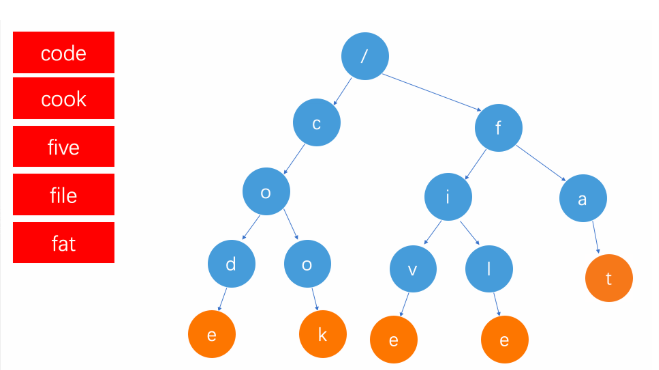
Trie树的实现
结点结构:
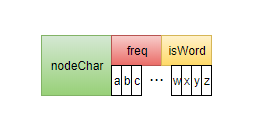
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| struct TrieNode {
char nodeChar;
int freq;
bool isWord;
vector<TrieNode*> childNode;
TrieNode()
{
freq = 0;
isWord = false;
childNode = vector<TrieNode*>(26,NULL);
}
};
|
树的大致结构:
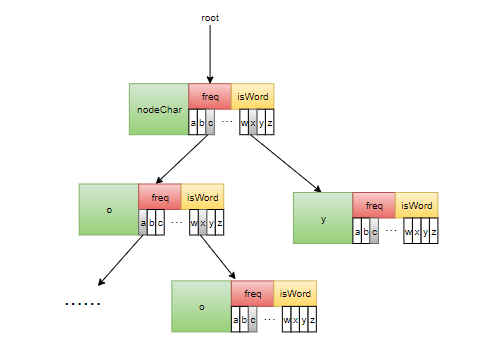
- 根节点的nodeChar不存储字符, 其字符表示位于指针数组中,指针数组的某元素不空则表示存在以其为首字符的单词。
添加操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
void addWord(TrieNode* root, string word, int k)
{
if(k >= word.size()) return;
int index = word[k] - 'a';
if(root->childNode[index] == NULL)
{
root->childNode[index] = new TrieNode();
root->childNode[index]->nodeChar = word[0];
if(k == word.size()-1)
{
root->childNode[index]->isWord = true;
}
addWord(root->childNode[index], word, k+1);
}
else
{
if(k == word.size()-1)
{
root->childNode[index]->isWord = true;
}
addWord(root->childNode[index], word, k+1);
}
}
|
查询操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
bool searchWord(TrieNode* root, string word)
{
TrieNode* p = root;
int i;
for(i = 0;i < word.size() && p != NULL;i++)
{
int index = word[i] - 'a';
if(p->childNode[index] == NULL)
{
return false;
}
else
{
if(i == word.size()-1)
p->childNode[index]->freq++;
p = p->childNode[index];
}
}
if(i == word.size() && p->isWord)
return true;
else return false;
}
|
删除操作
删除操作比较复杂,分三种情况:
1. 删除整个单词 (该单词的尾结点为叶子节点,且该单词独占一条路径)
2. 删除前缀词 (该单词的尾结点非叶子节点)
3. 删除分支单词 (该单词的尾结点为叶子节点但存在于其他单词共用的路径)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| bool isLeave(TrieNode* node)
{
for(int i = 0;i < 26;i++)
{
if(node->childNode[i] != NULL)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void deleteWord(TrieNode* root, string word, int k)
{
if(k >= word.size()) return;
cout << "delete into " << word[k] << endl;
int index = word[k] - 'a';
if(root->childNode[index] == NULL) return;
else
{
cout << 'd' << endl;
deleteWord(root->childNode[index], word, k+1);
if(isLeave(root) && !root->isWord)
{
cout << "dc" << endl;
delete root;
root = NULL;
}
else if(k == word.size()-1 && !isLeave(root))
{
root->isWord = false;
cout << "dd" << endl;
}
}
}
bool DeleteKey(TrieNode *root, string word)
{
if(searchWord(root, word))
{
deleteWord(root, word, 0);
return true;
}
return false;
}
|



